ATSB occurrence category taxonomy
The ATSB uses an occurrence category taxonomy to efficiently and consistently categorise and code transport safety occurrences. These occurrence categories can be used to search through occurrences in the ATSB’s National Aviation Occurrence Database.
A guiding principle behind the ATSB’s occurrence category taxonomy is that a relatively simple coding scheme greatly increases the quality of the data that is recorded in the occurrence database. The taxonomy follows a data-driven approach in that a particular occurrence category is only included in the taxonomy if either;
- it is an occurrence category commonly reported to the ATSB
- it is an uncommon but important occurrence category
The ATSB Occurrence Category taxonomy is a three-level hierarchy. In general, the structure of the hierarchy follows the ICAO ADREP 2000 model, and is divided into the following Level 1 Occurrence Type groupings;
- Operational – occurrences that relate specifically to aircraft operations that involve a human element
- Technical – occurrences that relate specifically to a failed aircraft component or system
- Airspace – occurrences that relate specifically to controlled and uncontrolled airspace issues
- Infrastructure – occurrences that relate specifically to the failure or anomalies with aerodrome and ATC facilities that directly affect an aircraft operation
- Environment – occurrences specifically related to external influences that have a direct impact on aircraft operations
- Consequential Events – occurrences that relate specifically to an operational necessity as the result of one of the other Level 1 groupings.
Each of the Level 1 Occurrence Category groupings is sub-divided into a number of related Level 2 groupings. In turn, Level 2 Occurrence Category groupings are further sub-divided into Level 3 groupings.
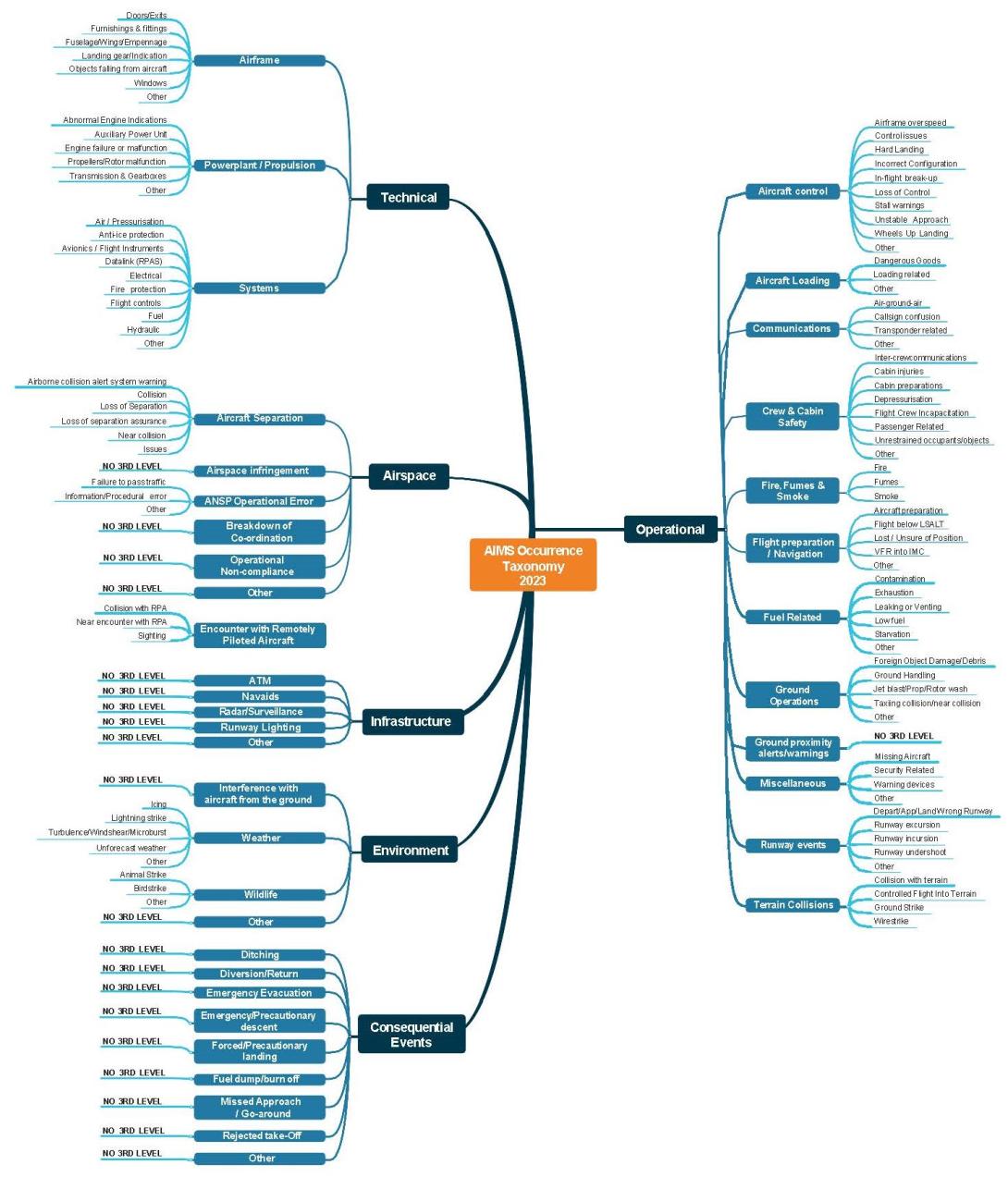
The hierarchical nature of the Taxonomy is of fundamental importance. It allows Level 3 data to be logically aggregated into Level 2 groupings, and then subsequently into Level 1 groupings. This is essential for higher-level data analysis.
In some cases an occurrence category may fall across two or more Level 1 groupings. Rather than create a specific coding for each Level 1 grouping, the hierarchy has been designed to capture it under the more common of the occurrence types.
Occurrence classifications
Prior to 31 December 2022
Accident: an occurrence involving an aircraft where:
- a person dies or suffers serious injury
- the aircraft is destroyed, or is seriously damaged
- any property is destroyed or seriously damaged.
Serious incident: an incident involving circumstances indicating that an accident nearly occurred (ICAO Annex 13).
Incident: an occurrence, other than an accident, associated with the operation of an aircraft which affects or could affect the safety of operation (ICAO Annex 13).
From 1 January 2023
Aircraft accident
A person suffers a fatal aircraft-related injury in relation to the operation of the aircraft; or
A person suffers a serious aircraft-related injury in relation to the operation of the aircraft; or
The aircraft sustains damage or structural failure, or there are reasonable grounds for believing that the aircraft has sustained damage or structural failure, which:
- Adversely affects the structural strength, performance or flight characteristics of the aircraft; and
- would normally require major repair or replacement of the affected component.
- Except for any of the following:
- Engine failure;
- engine damage limited to a single engine (including damage to its cowlings or accessories);
- damage to propellers, wing tips, antennas, probes, vanes, tyres, brakes, wheels, fairings, panels, landing gear doors or windscreens;
- damage such as small dents or puncture holes to the aircraft skin;
- minor damage to main rotor blades, tail rotor blades or landing gear;
- minor damage resulting from hail or bird strike (including holes in the radome); or
- the aircraft is missing; or
- the aircraft is completely inaccessible
Serious aircraft incident
A serious aircraft incident is an incident involving:
- Circumstances indicating that there was a high probability of an aircraft accident (that is, a high probability of a fatal or serious aircraft-related injury and/or the aircraft sustaining damage or structural failure); or
- an incident in the following table of incidents that have the potential to be classified as a serious incident.
Aircraft incidents
Any event that is associated with the operation of an aircraft and affects, or could affect, the safety of the operation of the aircraft.
The degree to which an occurrence “affects or could affect” the safety of the operation of the aircraft should be understood to mean occurrences that, if not corrected, could endanger the aircraft or its occupants. To be clear, a responsible person is required to report an aircraft incident whether or not it was actually corrected or able to be corrected.
Operation types
From 2 December 2021 the ATSB categorises operation types by the appropriate CASA flight operations regulations (CASR) Part number. Read more about the CASA flight operations regulations on the CASA website.
Part 91 General operating and flight rules
Part 101 Unmanned aircraft and rockets
Part 103 Sport and recreational aircraft
Part 105 Parachuting
Part 121 Australian air transport operations - Larger aeroplanes
Part 129 Foreign air transport operators
Part 131 Balloons and hot air airships
Part 132 Limited category aircraft
Part 133 Air transport operations - Rotorcraft
Part 135 Australian air transport operations - Smaller aeroplanes
Part 137 Aerial application operations
Part 138 Aerial work operations
Former operation types
(as applied to occurrences prior to 2 December 2021)
Air transport High capacity – operations conducted in aircraft refers to an aircraft that is certified as having a maximum capacity exceeding 38 seats, or having a maximum payload capability that exceeds 4,200 kg. Includes regular public transport (RPT), charter, check and training, test and ferry.
Air transport Low capacity – operations conducted in aircraft other than high capacity aircraft. That is, aircraft with a maximum capacity of 38 seats or less, or having a maximum payload capability of 4,200 kg or below. Includes regular public transport (RPT), check and training, test and ferry.
Charter – operations involving the carriage of passengers and/or cargo on non-scheduled flights by the aircraft operator, or by the operator’s employees, for trade or commerce (excluding regular public transport (RPT) operations).
Aerial work – includes ambulance, medivac, and other emergency medical service flights; and flying for the purposes of agriculture, mustering, search and rescue, fire control, or survey and photography. Includes commercial activities only.
Flying training – all commercial flying training operations.
Private – all private flying activities, including private (not for reward) operations involving mustering and training.
Business aviation – private operations conducted for the purpose of business.
Sports aviation – includes parachute operations, ballooning, warbird operations, and acrobatics.
Gliding – all non-powered and powered gliders.
Ballooning – all balloon operations.
Military – all operations where a military aircraft is involved.
Unknown/General aviation unknown – where the aircraft operation is unknown, generally due to the aircraft being involved in an airspace incursion or similar where air traffic control have not had aircraft details available.
Activity types
Commercial Air Transport
Scheduled
International – Scheduled operations of international airlines operating into/out of Australia (includes Qantas international not just foreign airlines, excludes flights to Australian territorial islands).
Domestic – Scheduled operations of domestic airlines operation within Australia (excludes foreign airlines conducting a domestic flight).
Scheduled freight only – Scheduled operations carrying freight only.
Unknown scheduled commercial air transport – Scheduled commercial operations where the activity subtype is unknown (unknown if the operator was conducting international, domestic or carrying freight only operations).
Non-scheduled
Passenger transport charters – Flying involving the carriage of passengers by the aircraft operator or their employees for hire or reward (excludes scheduled airlines operations, includes marine pilot transfers).
Medical transport – Operations as an aerial ambulance for the transport of ill or injured persons (excludes Angel flights).
Non-scheduled freight only – Flying involving the carriage of cargo by the aircraft operator or their employee for fire or reward (excludes scheduled airline freight operations).
Joyflight/sightseeing charters – Flying involving the carriage of passengers for joyflights or sightseeing purposes (includes warbird flights).
Other non-scheduled commercial air transport – Other non-scheduled commercial air transport operations not classified elsewhere (includes aircraft undertow or not board for flight).
Unknown non-scheduled commercial air transport – Non-scheduled commercial air transport operations where the activity subtype is unknown (unknown if the operator was conducting charter, medical transport, non-scheduled freight, joyflight/sightseeing or other non-scheduled operations).
Other commercial air transport
Other commercial air transport operation not classified elsewhere (includes aircraft under tow, not boarded for flight).
Unknown commercial air transport
Commercial air transport operation where the activity type is unknown.
General Aviation
Aerial work
Agricultural spreading/spraying – Flying involving the spreading/spraying of chemicals, seeds, and fertilisers (includes flights from the spreading/spraying area).
Agricultural mustering – Aerial stock mustering involving the direct use of aircraft for the movement of livestock.
Other agricultural – Other agricultural activity not classified elsewhere (includes aerial culling and baiting, bore and property inspections).
Unknown agricultural – Agricultural activity where the activity subtype is unknown.
Construction – sling loads – Flying using sling loads for construction purposes.
Other Construction – Flying for construction purposes (excludes sling loads).
Photography – All aerial photographic work (includes media filming operations).
Pipeline / powerline surveying – Aerial inspection patrols along pipelines or powerlines (includes insulator washing).
Other surveying – Flying involving the use of aircraft for surveying not classified elsewhere (including geophysical surveys).
Observation and patrol – Flying involving the use of aircraft for aerial observations and patrol (includes coastal surveillance, customs/border force patrols, traffic monitoring).
Search and rescue – Any search missions (includes evacuations or rescue work).
Policing – Flying involving the use of aircraft in police operations (includes traffic control, ground support, high-speed car pursuits, observation, air patrol).
Firefighting – Flying involving the use of aircraft to combat fires (e.g. spotting, water bombing) (includes flight to and from the fire area).
Advertising – Flying for of advertising purposes (includes skywriting and banner towing advertising).
Other aerial work – Aerial work flying not classified elsewhere (includes stock or fish spotting, cloud seeding, Military target towing, aerial refuelling, military support, medical clinics, radar/nav-aid calibration flights).
Unknown aerial work – Aerial work flying where the activity subtype is unknown.
Own business travel
Business flying not through hire or reward arrangement.
Instructional flying – Includes all training flights
Instructional flying – solo – Solo flying training for the issue or renewal of a licence or rating (includes solo navigation exercises conducted as part of a course of applied flying training).
Instructional flying – dual – Flying training (with an instructor) for the issue or renewal of a license or rating (includes aircraft type endorsement or conversion training).
Instructional flying – other – Instruction flying not classified elsewhere (includes search and rescue training, winching training, aircrew training, flight to maintain currency, load master training).
Instructional flying – unknown – Instruction flying where the activity subtype is unknown.
Sport and Pleasure flying
Glider towing – Flying involving an aircraft towing a glider.
Parachute dropping – Flying involving the dropping of parachutists.
Aerobatics – Flying with manoeuvres intentionally performed by an aircraft involving abrupt changes in altitude, abnormal altitude, or abnormal variation in speed (includes aerobatic displays, excludes competitions).
Pleasure and personal transport – Flying for private pleasure, or personal transport not associated with a business or profession (includes paragliding, recreational flying).
Community service flight – Flights that are provided on a voluntary basis for public benefit (includes Angel flights, non-emergency flights provided as part of an organised voluntary or charitable activity, excludes flights a pilot provides to a friend or family member).
Other sport and pleasure flying – Other sport and pleasure flying not classified elsewhere (includes air show, air racing or competition flying, excludes aerobatic displays).
Unknown sport and pleasure flying – Sport and pleasure flying where the activity subtype is unknown.
Other general aviation flying
Test flights – Flying associated with the testing of an aircraft.
Ferry flight – Flying associated with an aircraft delivery or movement to a location for maintenance, hire or other planned use (includes commercial airline aircraft).
Other flights – Other general aviation flying not classified elsewhere (includes demonstration flights of an aircraft with a potential buyer).
Unknown other flights – Other general aviation flight where the activity subtype is unknown.
Unknown general aviation flying
General aviation flight where the activity subtype is unknown.
Military
All flights where a military aircraft is involved.
Unknown activity group
Flying where the activity group is unknown.
Phase of Flight
Standing – Aircraft parked and boarded with the intention of flight
Taxiing – Aircraft moving on the ground under its own power
Take-off – Start of the take-off run to 50 feet above the runway
Initial climb – After take-off to a height of up to 3,000 ft AGL
Climb – Portion of flight above 3,000 ft AGL to ‘top of climb’
Cruise – Portion of flight between ‘top of climb’ and ‘top of descent’
Descent – Portion of flight from the ‘top of descent’ to 3,000 ft AGL
Approach – From 3,000 ft AGL to the runway threshold
Landing – From a position over the threshold to the position the aircraft stops on the runway.
Airspace types
CTA: Control area – a Controlled airspace extending upwards from a specified limit above the earth
CTR: Control zone – a controlled airspace surrounding aerodromes with active control towers that extend upwards from the surface of the earth to a specified upper limit.
CTAF: Common traffic advisory frequency – in the vicinity of non-towered aerodromes. CTAF refers to the designated frequency on which pilots make positional broadcasts.
OCTA: Outside controlled airspace
PRD: Includes:
- Prohibited areas – an airspace of defined dimensions, above the land areas or territorial waters of a State, within which the flight of aircraft is prohibited. Designation is appropriate only for reasons of military necessity.
- Restricted areas – airspace with defined dimensions, above the land areas or territorial waters of a State, within which the flight of aircraft is restricted in accordance with certain specified conditions.
- Danger area – an airspace of defined dimensions within or over which activities of potential danger to aircraft flying over the area may exist.
OCA: Oceanic control area
Airspace classes
A – Class A upper en route controlled airspace
- Within radar coverage – lower limit above FL180 and upper limit FL600;
- Outside radar coverage – lower limit FL245 and upper limit FL600; and
- an area extending from 190NM south of Melbourne to Launceston and Hobart, lower limit FL 180 and upper limit FL600.
C – Class C controlled mid-level en route (between class A and E) airspace and in the control area steps to, and the control zones around, major airports
- within radar coverage south of Sydney, lower limit FL 125 and upper limit FL 180 under Class A airspace;
- in the control area steps associated with controlled aerodromes, excluding control area steps classified as Class D airspace; and
- in control zones of defined dimensions.
D – Class D control area steps to, and control zones around, controlled metropolitan and regional airports
- control zones of defined dimensions, and associated control area steps, upper limit 4,500 FT.
E – Class E lower level controlled airspace
- within radar coverage:
- south of Sydney, lower limit 8,500 FT and upper limit FL 125 under Class C airspace;
- north of Sydney, lower limit 8,500 FT and upper limit FL 180 under Class A airspace;
- in the vicinity of Williamtown/Newcastle: coincident with the lateral limits of R578A-E above A045 - when R578 is not active;
- outside radar coverage within continental Australia, lower limit FL 180 and upper limit FL245 under Class A airspace;
- an area extending from 90 NM south of Melbourne to Launceston and Hobart, lower limit FL125 and upper limit FL 180 under Class A airspace; and
- in two corridors, Sydney to Dubbo, lower limit FL 125 and upper limit FL 180, under en route Class E airspace.
G – Class G is non-controlled airspace
- It is generally airspace between the ground and controlled airspace above, outside of the control zones and control areas surrounding controlled aerodromes. There is no air traffic separation service provided for any aircraft.
Foreign – Outside of the Australian Flight Information Region (FIR)
PRD – Prohibited, Restricted, or Danger area
Occurrence categories
Operational
Aircraft Control
- Airframe overspeed: The airspeed limit has been exceeded for the current aircraft configuration as published in the aircraft manual.
- Control issues: The flight crew encounter minor aircraft control difficulties while airborne or on the ground.
- Hard landing: The operational limits for the aircraft set out in the aircraft's operations manual are exceeded or damage occurs during the landing.
- Incorrect configuration: An aircraft system is incorrectly set for the current and/or intended phase of flight.
- In-flight break-up: Occurrences involving an airborne structural failure or damage to the airframe, including rotors, to the extent that sustained flight is no longer possible.
- Loss of Control: Occurrences where control of the aircraft is lost or there are significant difficulties controlling the aircraft either airborne or on the ground.
- Stall Warnings: Any cockpit warning or alert that indicates the aircraft is approaching an aerodynamic stall.
- Unstable Approach: A continued approach and/or landing in contravention of the operator SOP relating to their 'stable approach' criteria
- Wheels up landing: Occurrences involving a wheels-up landing when the gear is not lowered before contact with the intended landing area.
- Aircraft Control – Other: Aircraft control occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Aircraft loading
- Dangerous goods: The carriage of dangerous goods in contravention of Commonwealth, State or Territory law.
- Loading related: The incorrect loading of an aircraft if the loading adversely affected, or could have affected, any of the following:
- the aircraft's weight;
- the aircraft's balance;
- the aircraft's structural integrity;
- the aircraft's performance;
- the aircraft's flight characteristics. - Aircraft loading – Other: Aircraft loading occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Communications
- Air-ground-air: Communication difficulties between aircraft and Air Traffic Control, ground units or other aircraft, whether an aircraft is airborne or on the ground.
- Callsign confusion: Occurrences where an aircraft acknowledges and responds to an instruction issued to another aircraft, or an air traffic controller issues an instruction to the wrong aircraft.
- Transponder related: Occurrences relating to the incorrect setting of a code and/or usage of transponder equipment.
- Communications – Other: Communications occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Crew & cabin safety
- Inter-crew communications: Occurrences relating specifically to a loss or breakdown of communication between flight crew, cabin crew or associated ground staff from the time the aircraft is boarded for flight.
- Cabin injuries: A cabin crew member or passenger has suffered an illness or injury.
- Cabin preparation: Occurrences where the aircraft cabin has not been appropriately prepared for the current phase of flight.
- Depressurisation: Occurrences where the air pressure inside the cabin of a pressurised aircraft reduces to an extent that it requires intervening action by the flight crew.
- Flight crew incapacitation: A flight crew member is restricted to nil or limited duties as a result of illness or injury.
- Passenger related: Occurrences where the actions of a passenger adversely or potentially affects the safety of the aircraft.
- Unrestrained occupants / objects: Occurrences where aircraft occupants or objects are not appropriately restrained for the aircraft operation or phase of flight.
- Crew and cabin safety – Other: Cabin safety occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Fire, Fumes & Smoke
- Fire: Occurrences where a fire has been confirmed.
- Fumes: Occurrences where abnormal fumes or smells are reported on board the aircraft.
- Smoke: Occurrences where smoke is reported to be emanating from:
- internally within the aircraft; or
- is emitted from an external component of the aircraft; or
- a smoke alarm activates.
Flight preparation/Navigation
- Aircraft preparation: Errors or omissions during the planning phase including inflight planning that affect or might affect aircraft safety in relation to:
- the aircraft's weight;
- the aircraft's balance;
- the aircraft's structural integrity;
- the aircraft's performance;
- the aircraft's flight characteristics. - Flight below LSALT: An aircraft is operated below the designated or planned Lowest Safe Altitude (LSALT) for the in-flight conditions and phase of flight.
- Lost / unsure of position: Occurrences where flight crew are uncertain of the aircraft's position and request assistance from an external source.
- VFR into IMC: An aircraft operating under the Visual Flight Rules enters Instrument Meteorological Conditions.
- Flight preparation/Navigation - Other: Flight planning occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Fuel related
- Contamination: Occurrences where the presence of a foreign substance is found in fuel.
- Exhaustion: Occurrences where the aircraft has become completely devoid of useable fuel.
- Leaking or venting: Occurrences involving the loss of fuel from a fuel tank or fuel system.
- Low fuel: The aircraft's supply of fuel becoming so low (whether or not the result of a technical issue) that the safety of the aircraft is compromised.
- Starvation: Occurrences where the fuel supply to the engine(s) is interrupted, but there is still usable fuel on board the aircraft.
- Fuel – Other: Fuel related occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Ground operations
- Foreign object damage / debris: Any loose objects on a runway or a HLS or in an aircraft have caused, or have the potential to cause, damage to an aircraft.
- Ground handling: Any ground handling and aircraft servicing that caused, or have the potential to cause damage to the aircraft or injury.
- Jet blast / prop / rotor wash: Any air disturbance from a ground-running aircraft propeller, rotor or jet engine that has caused, or has the potential to cause, injury or damage to property.
- Taxiing collision / near collision: An aircraft collides with, or nearly collides with, another aircraft, terrain, person or object on the ground or on water, during taxi manoeuvring.
- Ground operations – Other: Ground operation occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Ground proximity alerts/warnings
- A ground proximity warning or alert.
Miscellaneous
- Missing aircraft: Occurrences where an aircraft is presumed to have crashed and the location of the crash is unknown.
- Security related: Occurrences where aviation security has been, or is likely to have been, compromised.
- Warning device other: The Warning device group of Occurrence Types cover situations in which an aural or visual aircraft warning device activates to alert the flight crew to a situation requiring immediate or prompt corrective action.
- Miscellaneous – Other: Miscellaneous occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Runway events
- Depart / Approach / Land wrong runway: An aircraft that takes off, lands, attempts to land from final approach or takes off from an area other than that authorised or intended for landing or departure.
- Runway excursion: Occurrences where an aircraft departs off the side or end of a runway during take-off or landing.
- Runway incursion: The incorrect presence of an aircraft, vehicle or person on the protected area of a surface designated for the landing and take-off of aircraft.
- Runway undershoot: Any aircraft attempting a landing and touches down prior to the threshold.
- Runway events – Other: Runway event occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Terrain collisions
- Collision with terrain: Occurrences involving a collision between an airborne aircraft and the ground or water, where the flight crew were aware of the terrain prior to the collision.
- Controlled flight into terrain (CFIT): Occurrences where a serviceable aircraft, under flight crew control, is inadvertently flown into terrain, obstacles, or water without either sufficient or timely awareness by the flight crew to prevent the event.
- Ground strike: Occurrences where a part of the aircraft drags on, or strikes, the ground or water while the aircraft is in flight, or during take-off or landing.
- Wirestrike: Occurrences where an aircraft strikes a wire, such as a powerline, telephone wire, or guy wire, during normal operations.
Technical
Airframe
- Doors/Exits: Occurrences where a door (passenger, cargo, or emergency), or its component parts, has exhibited damage or has failed.
- Furnishings and fittings: Occurrences where an internal aircraft furnishing or fitting (including its component parts), has exhibited damage or has failed.
- Fuselage / Wings / Empennage: Occurrences where the airframe has exhibited damage or has failed.
- Landing gear / Indications: Occurrences where aircraft landing gear, brakes (or their component parts) or tyres have exhibited damage, failed or the crew have received indications of a failure in the landing gear system.
- Objects falling from aircraft: Objects inadvertently falling from or detaching from an aircraft.
- Windows: Occurrences where a window of the aircraft has exhibited damage or has failed.
- Airframe – Other: Technical – Airframe occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Powerplant/Propulsion
- Abnormal engine indications: Occurrences involving indications that an engine is malfunctioning or operating outside normal parameters.
- Auxiliary Power Unit (APU): Occurrences involving a device on an aircraft that provides energy for functions other than propulsion.
- Engine failure or malfunction: An occurrence that results in a total engine failure, a loss of engine power or rough running.
- Propeller / Rotor Malfunction: Occurrences involving the failure or malfunction of an aircraft propeller/rotor or its associated components.
- Transmission and gearboxes: Occurrences where a transmission or gearbox has failed or malfunctioned.
- Powerplant / propulsion – Other: Powerplant / Propulsion occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Systems
- Air/Pressurisation: Occurrences involving partial or complete loss of normal functioning of an aircraft air system.
- Anti-ice protection: Occurrences involving partial or complete loss of systems on aircraft to prevent the formation of ice.
- Avionics / Flight instruments: Occurrences involving partial or complete loss of normal functioning of avionics systems or components.
- Datalink (RPAS): Occurrences involving the partial or total loss of transmission and/or reception of digital information from a remotely piloted aircraft system (RPAS).
- Electrical: Occurrences involving partial or complete loss of normal functioning of the aircraft electrical system.
- Fire protection: Occurrences involving partial or complete loss of normal functioning of the aircraft fire protection systems.
- Flight controls: Occurrences involving partial or complete loss of normal functioning of the primary or secondary flight control systems of an aircraft.
- Fuel: Occurrences involving partial or complete loss of normal functioning of an aircraft fuel system.
- Hydraulic: Occurrences relating to a partial or complete loss of an aircraft hydraulic system.
- Systems – Other: Technical – Systems occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Airspace
Aircraft separation
- Airborne collision alert system warning: Occurrences that result in an airborne collision avoidance system resolution advisory or equivalent type alert.
- Collision: Occurrences where there is a collision between two or more aircraft that are airborne, taking off or landing.
- Loss of separation (LoS): A failure to maintain a recognised separation standard (vertical, lateral or longitudinal) between aircraft that are being provided with an air traffic service separation service.
- Loss of separation assurance: An occurrence where separation has been maintained but has not been planned, actioned or monitored appropriately.
- Near collision: An aircraft that is airborne, taking off or landing comes into such close proximity with another aircraft, terrain, person or object where immediate evasive action was required or should have been taken.
- Aircraft separation – Issues: Airspace - Aircraft separation occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Airspace infringement
- Occurrences where there is an unauthorised entry of an aircraft into airspace for which a clearance is required.
ANSP operational error
- Failure to pass traffic: Occurrences where the ANSP fails to provide adequate traffic information to a pilot in relation to other aircraft. The information may have been incomplete, incorrect, late or absent.
- Information error: Occurrences involving errors in either the delivery or display of operational information by air traffic service officers.
- ANSP operational error – Other: Airspace – ANSP operational error occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Breakdown of Co-ordination
- Occurrences where air traffic service personnel have failed to exchange information, obtain agreement on clearances, process the transfer of control, advice or information to be issued to aircraft as necessary for the safe and efficient conduct of flight.
Operational non-compliance
- Occurrences where a pilot does not comply with a verbal instruction or published instruction as issued by air traffic service providers.
Airspace – Other
- Airspace occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Encounter with Remotely Piloted Aircraft
- Collision with RPA: Occurrences where an aircraft collides with an RPA either airborne or on the runway strip.
- Near encounter with RPA: Occurrences where an aircraft comes in close proximity to an RPA.
- Sighting: Occurrences where it is reported that an RPA was observed but no other aircraft was affected.
Infrastructure
Air Traffic Management (ATM) system
- Occurrences involving faults or deficiencies in the Air Traffic Management (ATM) system.
Navaids
- Occurrences involving faults or deficiencies in the operation of a navigation aid.
Radar / Surveillance
- Occurrences involving faults or deficiencies in the operation of a radar or surveillance system used for the purpose of separating aircraft in the air or on the ground.
Runway lighting
- Occurrences where aerodrome lighting is inadequate, or has failed.
Infrastructure – Other
- Infrastructure related occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Environment
Interference with an aircraft from the ground
- Any ground based activity that interferes with the operation of an aircraft.
Weather
- Icing: Occurrences where icing affects the performance of an aircraft.
- Lightning strike: Occurrences where an aircraft is struck by lightning.
- Turbulence: Occurrences where turbulence affects the safety of a flight.
- Windshear / Microburst: Occurrences where windshear or microburst phenomena affects the safety of a flight.
- Unforecast weather: Occurrences where weather conditions that were not forecast or not considered by the flight crew affect the safety of the flight.
- Weather – Other: Weather occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Wildlife
- Animal strike: Occurrences where an aircraft collides with an animal.
- Birdstrike: Occurrences where an aircraft collides with a bird.
- Wildlife – Other: Wildlife occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Environment – other
- Environmental related occurrences not specifically covered elsewhere.
Consequential events
Ditching
- Occurrences where an aircraft is forced to land on water.
Diversion / Return
- Occurrences where an aircraft does not continue to its intended destination, but either returns to the departure aerodrome or lands at an alternative aerodrome.
Emergency evacuation
- Occurrences where crew and/or passengers vacate an aircraft in situations other than normal and usually under the direction of the operational crew.
Emergency / Precautionary descent
- Emergency descent – Circumstances that require the flight crew to initiate an immediate high-rate descent to a specified altitude to ensure the continued safety of the aircraft and its occupants.
- Precautionary descent – Circumstances, other than an ATC clearance, that requires the flight crew to perform a controlled descent to a specified altitude to ensure the safety of the aircraft and its occupants.
Forced / Precautionary landing
- Forced landing – Circumstances under which an aircraft can no longer sustain normal flight and must land regardless of the terrain.
- Precautionary landing – a landing either on land or water made as a precaution, when in the judgement of flight crew, a hazard exists with continued flight.
Fuel dump / Burn off
- Occurrences where an aircraft dumps or burns off fuel in order to reduce its landing weight to an acceptable limit.
Missed approach / Go-around
- Occurrences in which the aircraft discontinues its approach to land.
Rejected take-off
- Occurrences where an aircraft discontinues the take-off.
Consequential event - Other
- Consequential events not specifically covered elsewhere.


